Page 8 - Oct-Dec 2017
P. 8
Wealth of Wadya
The invention and development of each
instrument has an interesting history.
anCIent dIvISIOnS mYStICaL mRIdangam
In the Natyashastra of Bharat Muni, Mridangam is an Indian
musical instruments are classified into percussion instrument. It is a
four groups – favourite of Lord Ganesha and
1. Tat Wadya: String instruments Nandi. It is also known as Illustration by: P. Dharani, IX
2. Sushir Wadya: Wind instruments “Deva Vaadyam” (Instrument A, Govt. Girls’ Hr. Sec. School,
Orthanadu, Thanjavur
3. awanadhha Wadya: Percussion of the Gods). It is a double-
instruments are covered with a Illustration by: Aanchal, XI, sided drum made of jackfruit
membrane mainly of the animal Pine Hall School, wood. The mouths are covered with goat skin.
skin Dehra Dun Divleen Singh, IX, Springdale Sr. School, Amritsar; Sahil Khanna, VIII D,
4. ghan Wadya: Solid instruments Sri Padampat Singhania education Centre, Kanpur
are made of hard materials such as metal, wood.
taPPIng taBLa
nOBLe nadaSwaRam Tabla consists of two drums, the
bayan and the dayan, almost always
Nadaswaram is a double reed wind played together. The top part of the Illustration by: Samriti, VIII,
instrument. It is considered drum is covered with goat skin. In Sri Sathya Sai Jagriti Vidya
as the world’s loudest non- the centre of the skin is the gab, a Mandir, Darwa, Yamuna
Nagar
brass acoustic instrument. It black circular area which helps in modulation.
is played during weddings and Illustration by: R. Hari Nethra, VIII,
temples in south India. Sri Seshaas International Public G. Sai Devi, VII b, Angappa educational Trust Sr. Secondary School,
School, Salem Coimbatore
StIRRIng SHeHnaI PLaYfUL PakHavaJ
Shehnai is a wind instrument Pakhavaj is a percussion instrument
from North India played from the Mughal Period. It is shaped like
during weddings. It is made a barrel with two heads. It is similar to the
of wood, with a double reed at one end and a metal or mridangam of South India. It is mainly used in Dhrupad
wooden flared bell at the other. It is similar to South India’s recitals.
Nadaswaram. b. Madhan, VIII A, Alpha english Higher Secondary School, Puducherry;
Shalini Soni, G D Goenka International School, udaipur
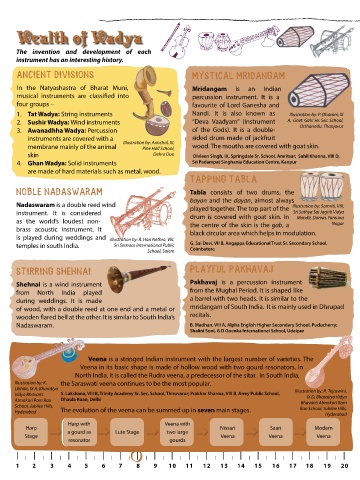
dIvIne veena
Veena is a stringed Indian instrument with the largest number of varieties. The
Veena in its basic shape is made of hollow wood with two gourd resonators. In
North India, it is called the Rudra veena, a predecessor of the sitar. In South India,
Illustration by: K. the Saraswati veena continues to be the most popular.
Likhita, IX A, Bharatiya Illustration by: R. Tejaswini,
Vidya Bhavan’s S. lakshana, VIII b, Trinity Academy Sr. Sec. School, Thiruvarur; Prakhar Sharma, VIII b, Army Public School, IX D, Bharatiya Vidya
Atmakuri Ram Rao Dhaula Kuan, Delhi Bhavan’s Atmakuri Ram
School, Jubilee Hills, Rao School, Jubilee Hills,
Hyderabad The evolution of the veena can be summed up in seven main stages.
Hyderabad
Harp with Veena with
Harp Nissari Saari Modern
Stage a gourd as Lute Stage two large Veena Veena Veena
resonator gourds
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20